Nowadays, nearly every sector is driven by artificial intelligence. However, this expansion requires responsible supervision, safety, and trust. This is why the international standards community developed its own framework for auditing and conformity evaluation in the form of ISO/IEC 42005 and ISO/IEC 42001.
While on the one hand, ISO/IEC 42001 outlines the characteristics of an effective AI governance system, ISO/IEC 42005 describes how to assess, audit, and certify that system appropriately.
Here we will take a look at everything you need to know about ISO/IEC 42005, including audit requirements, auditor competency, conformity assessment activities, and how it relates to ISO/IEC 42001 and ISO/IEC 23894.
Understanding ISO/IEC 42005 and Its Governance Role in AI Management
The international standard ISO/IEC 42005 describes the audit principles, procedures, and requirements for conformity assessment for assessing AI Management Systems (AIMS). It serves as ISO/IEC 42001’s companion, instructing auditors and organizations on how to determine whether an AI governance framework is:
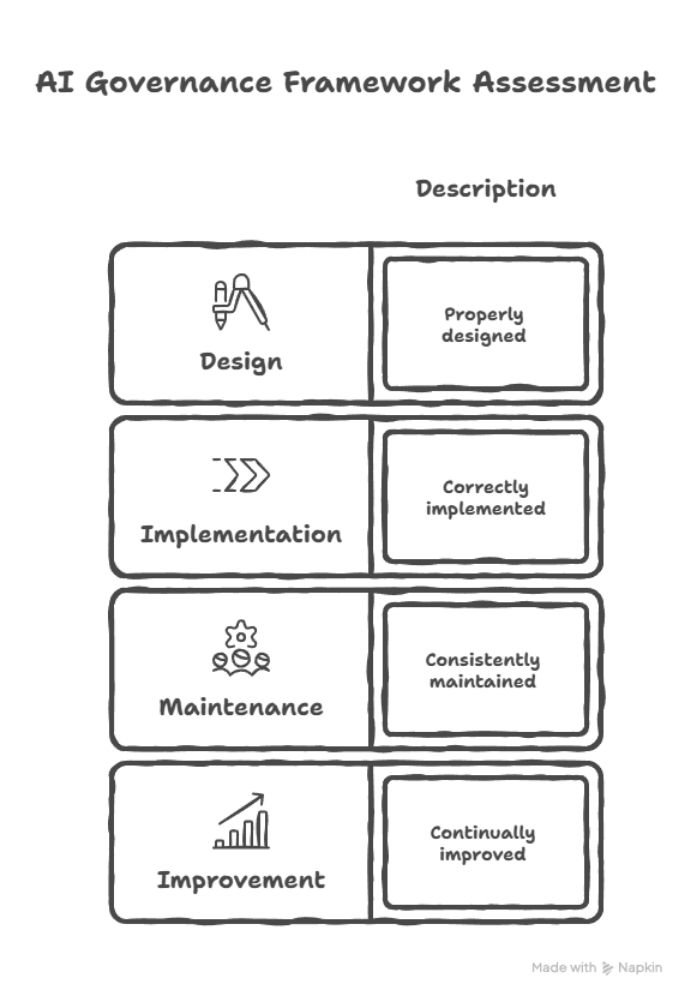
Basically, ISO/IEC 42005 makes sure that all the rules in ISO/IEC 42001 are verified through a structured audit approach.
One of the main reasons why this is important because AI systems are constantly dealing with:
- Personal data
- Automated decisions
- High-risk outcomes
- Ethical implications
- Safety and security risks
All these aspects combined make audits essential, showcasing whether or not an organization is meeting the global expectations for responsible AI.
How ISO/IEC 42005 Ensures Reliable Compliance with ISO/IEC 42001
While the ISO/IEC 42001 provides a great career and learning path, it also establishes a roadmap for developing an AI management system. However, third-party evaluations, surveillance audits, and internal audits that follow ISO/IEC 42005 provide the true evidence of compliance.
This standard ensures reliable compliance in the following ways:
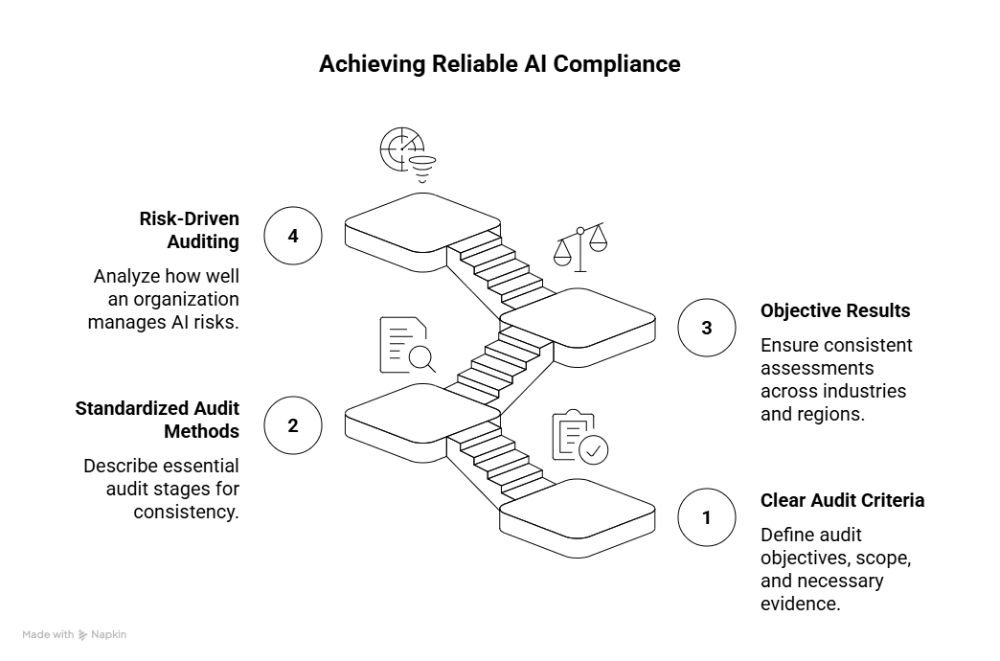
Core Audit and Conformity Objectives Defined in ISO/IEC 42005
Here is a look at the main audit and conformity objectives that have been defined in ISO/IEC 42005. These core objectives must be evaluated by auditors when assessing an AI Management System.
- Verify ISO/IEC 42001 compliance: Here, auditors check whether or not the company complies with the requirements, manages the AI lifecycle well, follows the procedures for AI risk management, documents the governance policies, and has operational protections in place. This is why it is important to understand how ISO/IEC 42001 strengthens AI governance and compliance frameworks.
- Verify the alignment of risk management: It is crucial that risks that are unique to AI need to adhere to ISO/IEC 23894’s guidelines. These risks can include:
- Data quality
- Drift of the model
- Fairness and bias
- Explainability
- Cybersecurity
- Assess the efficacy of governance: This could include:
- Structures for making decisions
- Functions and obligations
- Mechanisms for accountability
- Verify ongoing progress: Other aspects that organizations need to provide regular updates regarding include monitoring AI models, a new rule, better handling of potential Incidents, and stakeholder feedback.
- Assess organizational competence: Teams managing AI must demonstrate certain technical skills, risk awareness, and governance capability.
Clauses and Audit Requirements for Evaluating AI Management Systems
Clauses in ISO 42005 specify what an auditor has to look for when evaluating an AI management system.
The majority of audits assess the following areas:
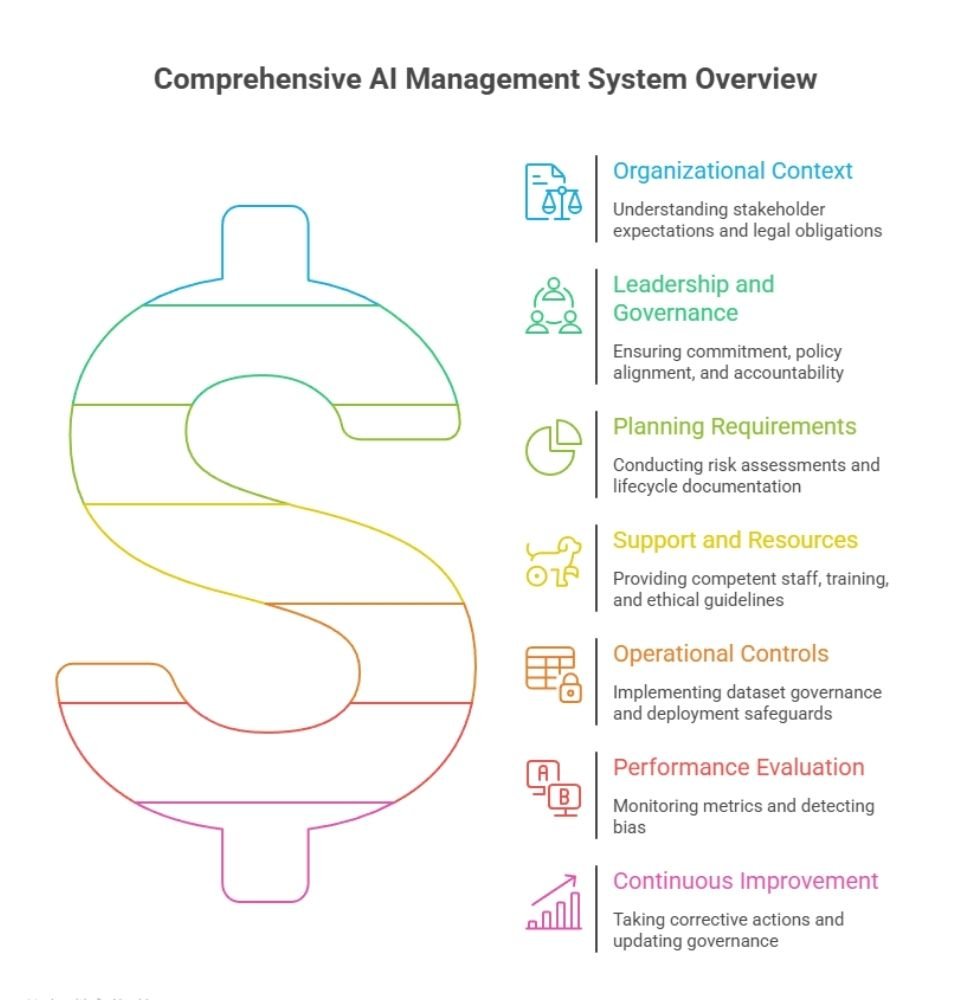
A solid basis for AI governance is provided by these organized ISO/IEC 42005 audit requirements.
Internal, External, and Surveillance Audits under ISO/IEC 42005
The ISO/IEC 42005 standard identifies three main audit categories for companies. These include:
1. Internal audits:
These internal audits help assess:
- gaps in compliance,
- risks associated with AI systems,
- quality of documentation,
- consistency in governance
Before applying for ISO/IEC 42001 certification, such internal audits are necessary.
2. External Certification Audits:
These audits are a bit different from internal audits. They:
- Offer impartial confirmation
- Lead to the gaining of official certification
- Provide worldwide legitimacy
- Verify the AIMS’s performance and design.
3. Surveillance Audits:
After the certification has been gained, these surveillance audits take place once a year. They verify whether the controls are still operational, risks are controlled, and AI systems continue to comply. These audits are necessary for continuous compliance and AI governance certification.
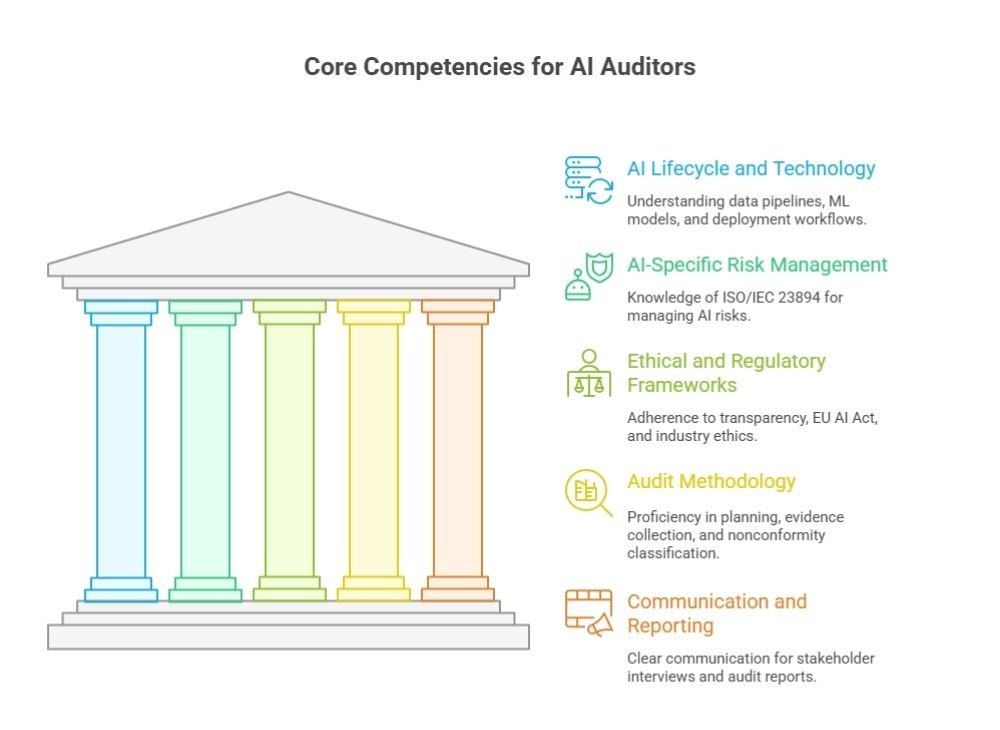
Competency Requirements for AI Management System Auditors
Compared to auditing conventional management systems, AI governance auditing is more complicated. An ISO/IEC 42001 lead auditor certification guide also helps in this aspect. Auditors must be knowledgeable about:
Responsibilities of Conformity Assessment Bodies in AI Governance Certification
In order to accredit organizations under ISO/IEC 42001, Accredited Conformity Assessment Bodies (CABs) are essential.
Some of the main duties of these bodies include:
1. Consistently implementing ISO/IEC 42005:
CABs must adhere to all audit rules, evidence requirements, and reporting expectations.
2. Ensuring auditor proficiency:
Accredited Conformity Assessment Bodies confirm that auditors adhere to the following aspects:
- Technical credentials
- Expectations for the experience
- Moral principles
3. Carrying out impartial audits
These bodies are always expected to steer clear of certain impartialities. These include:
- Conflicts of interest
- Prejudice
- Unfair evaluations
4. Preserving certification integrity
To preserve certification integrity, the CABs must take care of the following things:
- Maintaining records
- Audits of surveillance
- Procedures for recertification
5. Ensuring worldwide congruence
CABs need to adhere to ISO/IEC guidelines that support the maintenance of certain aspects. These include:
- Global trust
- Recognition across borders
- Compatibility with regulations
Integration of ISO/IEC 42005 with ISO/IEC 42001 and ISO/IEC 23894
What you need to understand is that ISO/IEC 42005 doesn’t work alone; it integrates with ISO/IEC 42001 and ISO/IEC 23894. Here is a look at how this happens.
1. ISO/IEC 42001: Requirements for AI Management Systems
The audit method for assessing adherence to all ISO/IEC 42001 provisions is provided by ISO/IEC 42005. This method aspects like includes:
- AI regulations
- Functions and obligations
- Management of the AI lifecycle
- Controls that are documented
- Risk mitigation strategies
2. AI Risk Management, ISO/IEC 23894
According to ISO/IEC 42005, auditors must assess whether companies follow ISO/IEC 23894’s risk management guidelines, which include:
- Identification of risks
- Analysis of risks
- Controls for bias and fairness
- Monitoring of uncertainty
- Evaluation following deployment
3. Model of Combined Governance
When combined, these guidelines assist businesses in creating:
- Safe AI systems
- Transparent decision-making
- Controls of ethics
- Preparedness for regulations
An AI governance framework that is both future-ready and globally reputable is guaranteed by this comprehensive approach. You can also take a more detailed look at the ISO/IEC 42001 certification guide to help you understand the process better.
Business and Regulatory Benefits of Implementing ISO/IEC 42005
Adopting ISO/IEC 42005 audit and compliance procedures benefits organizations in a number of ways. Here are a few of the benefits:
1. Improved regulatory alignment:
This aspect encourages adherence to new laws like the EU AI Act, the NIST AI Risk Management framework, and the national regulations for data protection.
2. Better risk mitigation:
These audits usually reveal issues like systemic weaknesses, vulnerabilities in the model, data inaccuracies, and concerns about bias.
3. Increased client confidence:
The certification signals certain things like security, responsibility, and openness.
4. Improved internal management
These improvements in internal management help enhance aspects like:
- Making decisions
- Records
- Monitoring procedures
5. A competitive edge
The ISO/IEC 42005 gives one a competitive edge in certain situations. This includes
- Government projects
- High-risk markets for AI
- Global operations
The Global Future of AI Auditing and ISO/IEC 42005 Adoption
Regulations pertaining to AI are changing quickly. However, certain things are becoming clearer globally, including:
- More governments want third-party AI evaluations.
- Risk-based governance will be expected by regulators.
- AI systems that pose a high danger will require certification.
- Standardized reporting will become the norm for organizations.
This indicates that, like ISO/IEC 27006 for information security, ISO/IEC 42005 will probably become the global standard for responsible AI evaluations.
Key Takeaways for Organizations Pursuing ISO/IEC 42001 Certification
Here are some things to keep in mind if your company intends to obtain ISO/IEC 42001 certification:
- ISO/IEC 42005 is crucial: It outlines the audit guidelines that are used to assess your AI governance framework.
- Good documentation is important: Auditors can check compliance more quickly with clear proof.
- AI risk management needs to adhere to ISO/IEC 23894: During audits, this is a primary focus.
- Internal audits help you get certified: They draw attention to inadequacies early on.
- The skill of auditors is crucial: Certification is made easier by qualified specialists under ISO/IEC 42005.
- Organizations can accelerate readiness through training: Teams must understand certain things, including:
- The AI lifecycle.
- Mitigation of bias
- Risk management
- Policies for governance
Teams can be properly prepared with the aid of GAICC’s ISO/IEC 42001 training programs as well.



